Crystal structure of Synechococcus phycocyanin: implications of light-harvesting and antioxidant properties.
Patel, S.N., Sonani, R.R., Chaubey, M.G., Gupta, G.D., Singh, N.K., Kumar, V., Madamwar, D.(2023) 3 Biotech 13: 247-247
- PubMed: 37366498
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03665-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7D6W - PubMed Abstract:
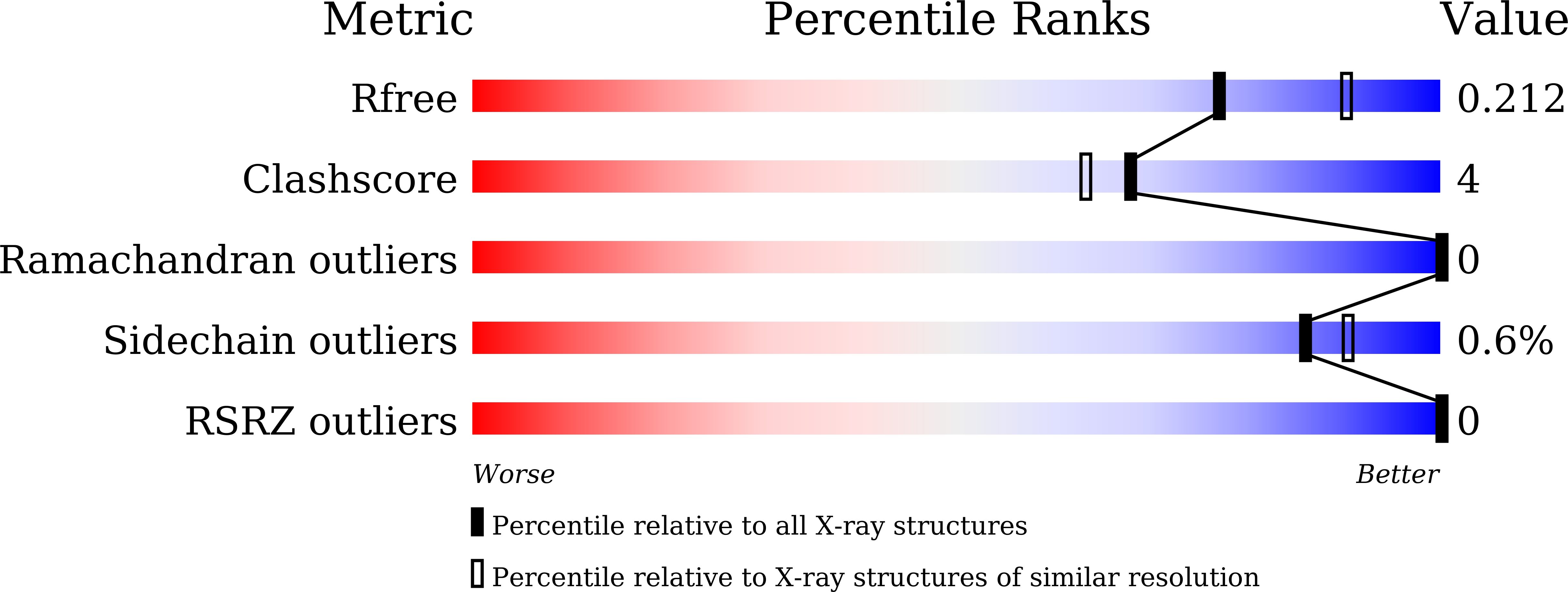
Phycobiliproteins is a family of chromophore-containing proteins having light-harvesting and antioxidant capacity. The phycocyanin (PC) is a brilliant blue coloured phycobiliprotein, found in rod structure of phycobilisome and has been widely studied for their therapeutic and fluorescent properties. In the present study, the hexameric assembly structure of phycocyanin (Syn-PC) from Synechococcus Sp. R42DM is characterized by X-ray crystallography to understand its light-harvesting and antioxidant properties. The crystal structure of Syn-PC is solved with 2.15?? resolution and crystallographic R -factors, R work / R free, 0.16/0.21. The hexamer of Syn-PC is formed by heterodimer of two polypeptide chains, namely, ¦Á- and ¦Â-subunits. The structure is analysed at atomic level to reveal the chromophore microenvironment and possible light energy transfer mechanism in Syn-PC. The chromophore arrangement in hexamer, deviation angle and distance between the chromophore contribute to the energy transfer efficiency of protein. The structural attributes responsible for the antioxidant potential of Syn-PC are recognized and annotated on its 3-dimensional structure. The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03665-1.
Organizational Affiliation:
P. D. Patel Institute of Applied Sciences, Charotar University of Science and Technology, CHARUSAT Campus, Changa, Anand, Gujarat 388421 India.